- Announcements
- Objectives
- Textbook
- Grading
- Course Conduct
- Course Material
- Supplementary Material
- Schedules
- Weekly Coverage
- Contact
Announcements
About Add-drop Period: Tomorrow at 3 pm the course will be open for all students who are on probation. Please find a section that is both empty and suits your schedule fully (in terms of both lecture hours and especially lab hours). We are not going to change your sections even if you mistakenly register and create a scheduling conflict.
- Midterm date: 2nd of December 17:40.
- Final date: 6th of January 13:30.
Objectives
This course gives a brief introduction to a working understanding of basic computer organization, data representation, programming language constructs, and algorithmic thinking. It is designed as a first course of programming and supported by laboratory sessions for students outside of the Computer Engineering major.
Textbook
Programming with Python for Engineers, by S. Kalkan, O. T. Şehitoğlu and G. Üçoluk. Available at: https://pp4e-book.github.io/
Grading
| Attendance | 10% |
| Midterm | 30% |
| Labs | 30% |
| Final | 30% |
Course Conduct
The flow of this course has 2 hours of in-class (theoretical) lectures + 2 hours of laboratory work. In addition, the theoretical part has Midterm and Final exams.
This has been altered as follows:
Weekly:
- In a pre-scheduled (see: Schedule section below) session, the lecturer will perform the subject review and a recitation (going over programming examples) of that week’s topics.
- Starting with the 4th week, there will be a lab session held at MM-14. Here the students will be given a programming environment and a task that they will code in a given duration.
About Exams:
- Midterm exam and final exam will be in class.
Course Material
-
Course Textbook [Available at: https://pp4e-book.github.io/] This is an ‘interactive’ book with a rather ‘minimalist’ approach: Some details or specialized subjects are not emphasized and instead, direct interaction with examples and problems are encouraged. Therefore, rather than being a ‘complete reference manual’, this book is a ‘first things first’ and ‘hands on’ book. The pointers to skipped details will be provided by links in the book. Bearing this in mind, the reader is strongly encouraged to read and interact all contents of the book thoroughly.
The book’s interactivity is thanks to Jupyter notebook. Therefore, the book differs from a conventional book by providing some dynamic content. This content can appear in audio-visual form as well as some applets (small applications) embedded in the book. It is also possible that the book asks the reader to complete/write a piece of Python program, run it, and inspect the result, from time to time. The reader is encouraged to complete these minor tasks. Such tasks and interactions are of great assistance in gaining acquaintance with Python and building up a self-confidence in solving problems with Python.
You can download the PDF of the course textbook from https://pp4e-book.github.io/.
Of course, the PDF does not provide the dynamic content.
-
Course Workbook [Available at: https://pp4e-workbook.github.io/] This is also a Jupyter book that is coherent with the course textbook. It contains solved and unsolved exercises in Python which are tagged with difficulty levels [between ★ and ★★★★★]. Students are strongly advised to work, level by level, through the solved exercises then proceed to the unsolved ones.
-
Python Interpreter
There are two alternatives to practice Python:
-
Installing a Python 3 Interpreter on your personal computer.
-
Using an interpreter accessible on the Web.
-
This alternative is the environment the book is written on, i.e. Google Colab: https://colab.research.google.com.
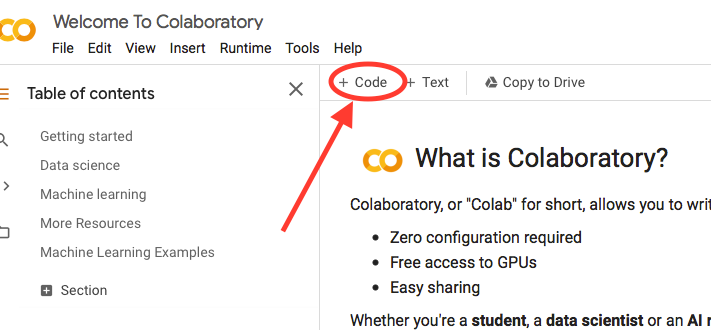
After cancelling the entry page, you arrive at a page which looks like the one above. Click “+ Code” tab and you will see at the bottom a freshly created cell. You can type in that cell your Python code and run it by hitting the small arrow
 at the left top of that cell.
at the left top of that cell. -
Another alternative is to use another online interpreter:
- https://www.python.org/shell/
- http://www.pythontutor.com/visualize.html#mode=edit
- https://www.programiz.com/python-programming/online-compiler/
- https://repl.it/repls/TechnicalOverjoyedDesignmethod#main.py
- http://pythonfiddle.com
- https://www.ideone.com
- https://www.programiz.com/python-programming/online-compiler/
- https://rextester.com/runcode
- https://www.onlinegdb.com/online_python_interpreter
- https://mathcs.holycross.edu/~kwalsh/python/
- http://techmums.co/python.html
-
-
Supplementary Material
Useful links on WEB [mostly from wiki.python.org]
- Tutorials and Websites
- A Byte of Python, by Swaroop C.H., is also an introductory text for people with no previous programming experience.
- After Hours Programming Python 3 Tutorial
- An App to Learn Python - A beginner-friendly app on Android and iOS to learn Python step by step with in-built interpreter and quizzes.
- Ask Python Absolute Beginners Python Tutorial
- Beginner-friendly guide to Python, that starts with the absolute basics but goes on to more advanced stuff as well
- Classpert - Python - A large collection of free and paid Python online courses, from a wide range of providers.
- Hackr.io - Python: Programming community-recommended best Python tutorials and courses
- Hands-on Python Tutorial Beginners’ Python, graphics, and simple client/server introduction, with videos
- Learning to Program An introduction to programming for those who have never programmed before, by Alan Gauld. It introduces several programming languages but has a strong emphasis on Python. (Python 2 and 3)
- Letsfindcourse - Python: Best Python tutorials and courses recommended by experts.
- The Wikibooks Non-Programmer’s Tutorial for Python by Josh Cogliati
- Learn Python An Introductory yet in-depth tutorial for Python beginners.
- Learning to Program by Alan Gauld
- The Python tips blog includes Python tips and tutorials for beginners and professional programmers.
- Python Tutorial in Python’s documentation set. It’s not written with non-programmers in mind, but it will give you an idea of the language’s flavor and style.
- The Python-Course.eu’s extensive tutorial for complete beginners, with lots of illustrations.
- Pythonspot Tutorials Python tutorials.
- The Python Guru A beginner-friendly guide for aspiring programmers.
- CodersLegacy A website + blog geared towards both new and experienced programmers. Mainly focused on teaching Python.
- The Codezine A python programming blog built for beginners.
- Top Courses to Learn Python - gitconnected.com Python tutorials submitted and ranked by Python developers with the best rising to the top
- Coursesity - Python - Curated list of the best python courses and tutorials for beginners.
- BeginnersGuide/Programmers
- https://realpython.com/python-first-steps/
- https://python.swaroopch.com
- https://www.learnpython.org
- Interactive Courses
- CheckiO is a gamified website containing programming tasks that can be solved in Python 3.
- Codecademy (Python)
- Code the blocks combines Python programming with a 3D environment where you “place blocks” and construct structures. It also comes with Python tutorials that teach you how to create progressively elaborate 3D structures.
- Computer Science Circles has 30 lessons, 100 exercises, and a message system where you can ask for help. Teachers can use it with their students. It is also available in Dutch, French, German, and Lithuanian.
- DataCamp Python Tutorial Unlike most other Python tutorials, this 4 hour tutorial by DataCamp focuses on Python specifically for Data Science. It has 57 interactive exercises and 11 videos.
- Finxter - How good are your Python skills? Test and Training with >300 hand-picked Python puzzles.
- HackInScience - 50+ Python exercises on a free, adless, simple, and open-source platform.
- How to Think Like a Computer Scientist: Interactive Edition is an interactive reimagination of Elkner, Downey and Meyer’s book with visualizations and audio explanations.
- Books
-
Automate the Boring Stuff with Python - Practical Programming for Total Beginners by Al Sweigart is “written for office workers, students, administrators, and anyone who uses a computer to learn how to code small, practical programs to automate tasks on their computer.” website print version -
How To Think Like a Computer Scientist is a classic open-source book by Allen Downey with contributions from Jeffrey Elkner and Chris Meyers. It was updated to Python 3 by Peter Wentworth. website print version -
Making Games with Python & Pygame by Al Sweigart introduces the Pygame framework for novices and intermediate programmers to make graphical games. website print version
-
- Videos
- Python Programming Tutorials for Beginners: Installation, IDE, variables, functions, strings, lists, OOP
- The Young Programmers Podcast contains video lessons on Python, Pygame, Jython, Scratch, Alice, Java, and Scala.
- Tools
Interesting links on WEB
- https://thinkygames.com/games/the-farmer-was-replaced/
Schedules
| DEPT | SECTION | PLACE | LECTURER | TIME |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME | 1 | G111 | Hazal Mogultay Ozcan | Monday 15:40-17:30 |
| ME | 2 | YP-A2 | Sercan Pekin | Friday 13:40-15:30 |
| METE | 3 | U2 | Guven Fidan | Tuesday 15:40-17:30 |
| FDE | 4 | YP-A2 | Hakan Gursoy | Friday 15:40-17:30 |
| MATH | 5 | BMB1 | Kadir Ekmekci | Friday 13:40-15:30 |
| MHED & EE | 6 | U1 | Huseyin Sayin | Wednesday 08:40-10:30 |
| EE & IE | 7 | BMB3 | Gokhan Orhan | Thursday 13:40-15:30 |
| EE | 8 | U1 | Furkan Murat | Thursday 15:40-17:30 |
| IE | 9 | G111 | Hazal Mogultay Ozcan | Monday 13:40-15:30 |
Weekly Coverage
Week 1 (29.09)
- Lecture Topics:
- Introduction: Course content, objectives, outline; Grading; Information about the homeworks, the labs, the exams.
- Basic computer organization: Von Neumann arch, CPU, RAM and their interaction during program execution, stored program, Peripherals, OS.
- Lab Topics: No Labs.
Week 2 (06.10)
- Lecture Topics:
- A Broad Look at Programming and PL: Concept of Algorithm, Comparing algorithms, World of PLs, Low-High level PL, Interpreter vs Compiler, Programming Paradigms, Python as a PL.
- Representation of data in computers: Two’s complement representation of integers, IEEE floating-point representation, Information loss with Floating Points, representation of characters, text and Boolean.
- Lab Topics: No Labs.
Week 3 (13.10)
- Lecture Topics:
- Introduction to Python: Numbers and Boolean values in Python, Container data in Python (str, tuple, list, dict, set); Mutable - immutable data; aliasing problem.
- Lab Topics: No Labs.
Week 4 (20.10)
- Lecture Topics:
- Introduction to Python [continued]: Operators and Expressions; Type casting; Statement in Python; Variables and Assignment; Basic I/O in Python.
- Lab Topics: Demo Labs.
Week 5 (27.10)
- Lecture Topics:
- Conditional & repetitive execution in Python: if statements; conditional expression; while & for statements; continue & break; List comprehension; Example problems.
- Lab Topics: No Labs.
Week 6 (03.11)
- Lecture Topics:
- Conditional & repetitive execution in Python [continued]: if statements; conditional expression; while & for statements; continue & break; List comprehension; Example problems.
- Lab Topics: Expressions, Variables, Basic I/O.
Week 7 (10.11)
- Lecture Topics:
- Functions: Defining functions; Passing parameters; Scope of variables; Recursion; Example definitions.
- Lab Topics: No Labs.
Week 8 (17.11)
- Lecture Topics:
- Functions [continued]: Defining functions; Passing parameters; Scope of variables; Recursion; Example definitions.
- Lab Topics: If statement, conditional expression.
Week 9 (24.11)
- Lecture Topics:
- Object-oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts: Class definition; Member functions & variables; Message passing; Encapsulation; Inheritance; Polymorphism; Basics of OOP in Python.
- Lab Topics: Conditional and repetitive statements & expressions.
Week 10 (01.12)
- Lecture Topics:
- File handling: Files and Sequential access; Parsing; Termination of Input; Formatting output; binary files.
- Lab Topics: Repetitive execution & functions (I)
Week 11 (08.12)
- Lecture Topics:
- Exception handling and Debugging: Kind of errors; Exceptions; Debugging techniques.
- Lab Topics: Repetitive execution & functions (II)
Week 12 (15.12)
- Lecture Topics:
- Engineering and scientific libraries for Python: Libraries and tools for numerical & scientific calculations (arrays, n-D arrays, slicing, basic operations on arrays, commonly used functions, algebraic functions etc.).
- Lab Topics: OO operations on built-in objects.
Week 13 (22.12)
- Lecture Topics:
- Engineering and scientific libraries for Python [continued]: Data handling & analysis, and plotting. Illustration of these tools with examples.
- Lab Topics: File handling.
Week 14 (29.12)
- Lecture Topics:
- An Application: Approximation & optimization.
- An Application: Solving a simple regression problem.
- Lab Topics: No Labs.
Contact
Please use the following email address for course related issues: ceng240 [@] ceng [dot] metu [dot] edu [dot] tr